Cloud computing relies heavily on data centers in 2025, which fuel apps, platforms, and the underlying infrastructure. There are different types of public cloud data centers for shared use, private cloud data centers for single organizations, and hybrid cloud data centers that mix both. Edge data centers bring services closer to users for faster performance, while enterprise data centers are owned and run by individual Big Tech Data Center Companies.
Today, lots of businesses use cloud colocation to place their servers in third-party cloud data center facilities, saving money and improving reliability. Leading data center companies offer flexible, secure, and high-speed solutions to meet growing cloud demands. In this year 2025, edge data center growth and smart cloud data center use are rebuilding the future of cloud computing.
What is a Data Center in Cloud Computing?
A data center in cloud computing is a machine that stores data and manages servers, storage systems, and networking equipment and devices needed to run cloud services. It powers things with websites, apps, and data backups for them in a secure and reliable place. In cloud computing, instead of buying and managing their equipment, the Largest data center companies use cloud data centers run by big providers to offer services with Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud.
They are smarter, faster and more energy efficient. The traffic, the security, and even power can be managed using AI. These data centers are located around the world, so users can access cloud services quickly from anywhere. They also support and maintain cloud colocation, allowing businesses to place their equipment in shared facilities for better performance and lower costs.
Role of Data Centers in Cloud Computing
Data centers play a key role in cloud computing by offering the physical and digital space where cloud services run. They support and monitor everything from social media and e-commerce websites to business software by hosting powerful computers, storage systems, and networks. Typically this setup, referred to as data center infrastructure, allows users to access the apps and data no matter what device they may be using or where they may be in the world.
Modern cloud services rely on advanced data center network architecture to move data quickly and safely. These centers also offer large data storage solutions to handle the growing amount of digital information. In 2025, many companies will turn to smart, scalable data center solutions to keep their cloud systems fast, reliable, and secure, forming the strong foundation behind today’s digital world.
How is data center processing in cloud computing?
Data centers in cloud computing provide the hardware and software that serve as the basis for running services over the internet. To provide computing power, cloud providers utilize huge server, storage, and network facilities. The number of virtual machines that can run on one physical server is more efficient resource use. Tools like data center automation software help manage and scale these sources quickly for users.
To keep services fast and reliable, providers use data center optimization techniques for better storage, networking, and energy use. Data is backed up and protected with strong security systems. In 2025, companies like Microsoft are increasing AI data center spending to build smarter and more efficient cloud data centers that power the future of digital services.
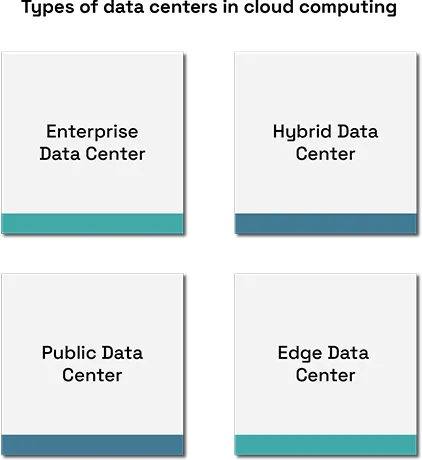
Types Of Data Centers In Cloud Computing.
Public Cloud Data Centers They are owned and operated by cloud providers that provide services such as, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud. They use the internet to offer computing power, storage and services to many customers.
Private Cloud Data Centers are used by a single organization to serve its own computing needs. They may be on-site or run by a third party. Public cloud data centers offer more control and customization than they do.
Hybrid Cloud Data Centers combine both public and private cloud features. They allow data and applications to move between the two, giving businesses flexibility for workloads and better handling of sensitive data.
Edge Data Centers are also known as small data centers set up near people who use the service. They help with low latency and speed (especially for IoT, video streaming, etc., or any other real-time services).
Enterprise Data Centers are run by large companies for their own IT utilization and vary in size and in the way they are set up, depending on the organization’s own requirements and resources.